Just to correct the previous answer. Frame Conductance is different from U-value in that it does not include air film.
For example, the U-value of Aluminum Frame in the library of Berkeley Lab WINDOW Program is 5.680 [W/m2·K].
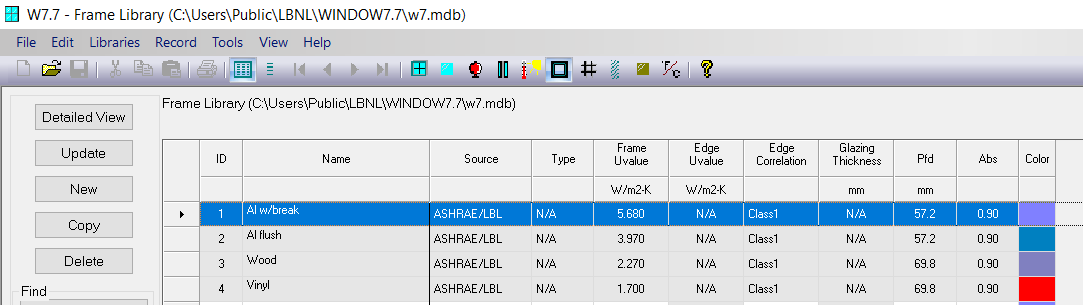
The Frame Conductance of this Aluminum Frame can be hand-calculated as follows.
Frame Conductance = 1 / {(1/Frame Conductance) - (R-value of outdoor air film) - (R-value of indoor air film)}
R-values of Air Film which are used in EnergyPlus are as follows.
All exterior conditions 0.0299387 [m2·K/W]
Interior vertical surfaces 0.1197548 [m2·K/W]
Then, the calculation above is
Frame Conductance = 1 / (1/5.68 - 0.0299387 - 0.1197548) = 37.9321831 [W/m2·K]
It's quite different from the U-value of 5.680 [W/m2·K].
Alternatively, some users recommend exporting IDF files which include Frame Conductance by the WINDOW Program. The exported Frame Conductance of the Aluminum Frame above is 56.42384 [W/m2·K], which is different from the hand-calculation above because WINDOW Program uses different air film resistances to EergyPlus.
All exterior conditions 1/30 = 0.033333333 [m2·K/W]
Interior surfaces 1/8 = 0.125 [m2·K/W]
Frame Conductance exported by the WINDOW Program = 1 / (1/5.68 - 0.033333333 - 0.125) = 56.42384 [W/m2·K]
In this case, 56.42384 [W/m2·K] seems more appropriate as the U-value of Aluminum Frame (5.680 [W/m2·K]) is from the WINDOW Program and it should be based on the air film resistances used in the WINDOW Program. When we get U-value data of window frames, we should be careful what air film resistances are based on.