First time here? Check out the Help page!
 | 1 | initial version |
ISO 13790 is a precedent version of ISO 52016. Many have tested and reported the percent differences of monthly aggregated heating and cooling demand between a well implemented ISO model (such as the EPC calculator by Georgia Tech) and EnergyPlus is within 5%.
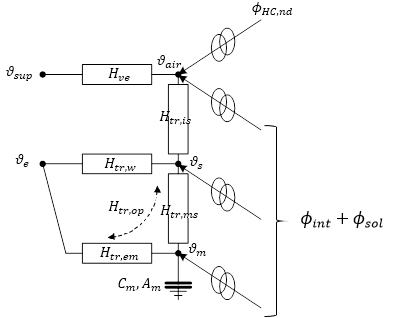
The ISO model has a interior surface node (θs) that is connected to the air node (θair).
The operative temperature can be calculated with the following equation per EN ISO 13790 C.12:
θop = 0.3 × θair + 0.7 × θs
The operative temperature is a weighted average of the air and mean radiant temperatures, weighted by the internal surface convective (3/8) and radiative coefficients (5/8). The value of θs is a mix between air and mean radiant temperature.
 | 2 | No.2 Revision |
ISO 13790 is a precedent version of ISO 52016.
Many have tested and reported the percent differences of monthly aggregated heating and cooling demand between a well implemented ISO model (such as the EPC calculator by Georgia Tech) and EnergyPlus is within 5%. 5-10%.
The ISO model has a interior surface node (θs) that is connected to the air node (θair).
The operative temperature can be calculated with the following equation per EN ISO 13790 C.12:
θop = 0.3 × θair + 0.7 × θs
The operative temperature is a weighted average of the air and mean radiant temperatures, weighted by the internal surface convective (3/8) and radiative coefficients (5/8). The value of θs is a mix between air and mean radiant temperature.

