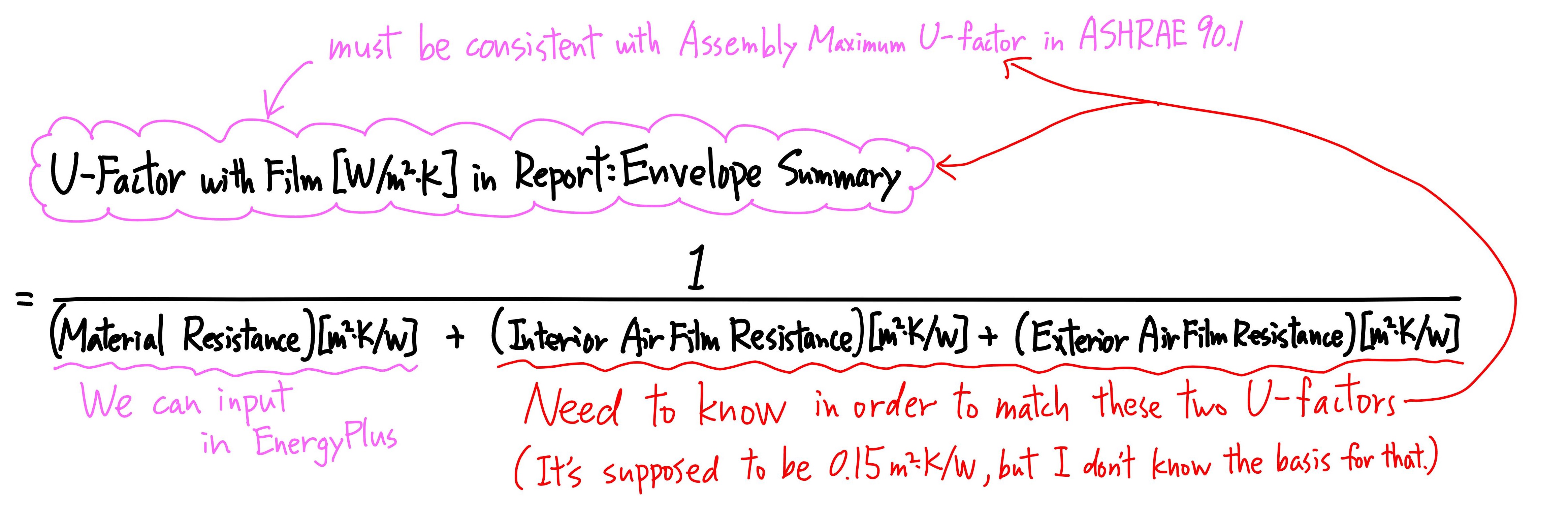
ASHRAE 90.1 prescribes assembly maximum U-factors for walls and roofs, and the U-factors need to be used for baseline case.
From the definition of U-factor in ASHRAE 90.1, it includes resistances of interior air film and exterior air film.

U-Factor with Film [W/m2·K] can be found in Report: Envelope Summary. I think we must match U-Factor with Film with the assembly maximum U-factor prescribed in ASHRAE 90.1 for baseline case.
However, Thermal Resistance [m2·K/W] in Material:NoMass does Not include Interior/Exterior Air Film Resistances. The input Thermal Resistance is equal to the reciprocal of U-Factor no Film.
Therefore, in order to match U-Factor with Film with the assembly maximum U-factor prescribed in ASHRAE 90.1, we need to know the Interior Air Film Resistance and Exterior Air Film Resistance that are used to calculate U-Factor with Film. Please refer to my sketch below.
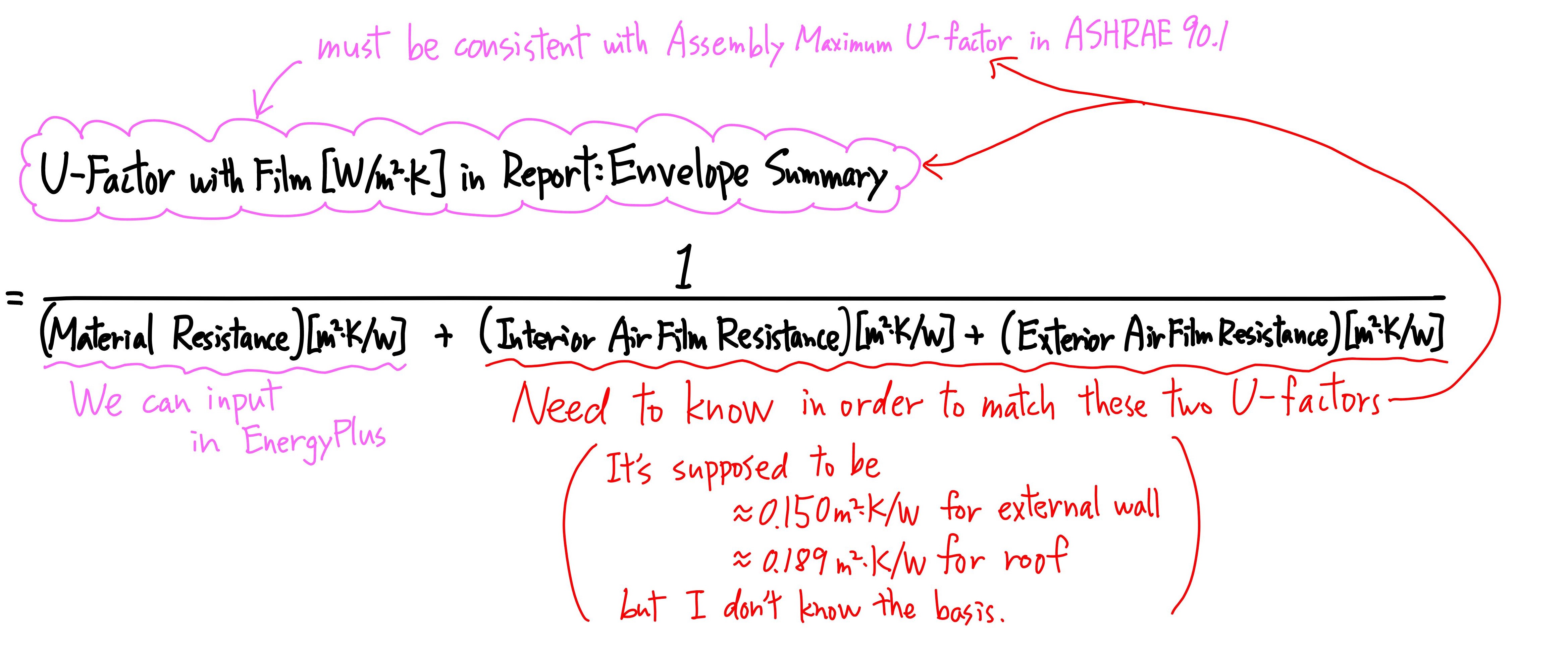
I know that air film resistance is calculated for each time step based on weather data during energy simulation. But for this U-Factor with Film, I did some case studies with different Thermal Resistance and different weather data, calculated (Interior Air Film Resistance) + (Exterior Air Film Resistance) from the above equation, and found that (Interior Air Film Resistance) + (Exterior Air Film Resistance) was always about 0.150[m2·K/W] for external wall and about 0.189[m2·K/W] for roof. They had nothing to do with weather data. But I don't know what is the basis for these Air Film Resistances? Does anyone know how they are calculated?
I may have overlooked it, but I couldn't find the basis in EngineeringReference and I/O Reference. If possible, I want to know each value of Air Film Resistance: Interior Air Film Resistance and Exterior Air Film Resistance.
P.S.
I noticed my mistake, so please let me correct it.
(Interior Air Film Resistance) + (Exterior Air Film Resistance) for roof is not about 0.189[m2·K/W] but about 0.1373[m2·K/W]. Interior Air Film Resistance for roof is 0.1074271[m2K/W], and Exterior Air Film Resistance for roof is 0.0299387[m2K/W].
In my case study, I mistakenly selected Surface as Outside Boundary Condition of the roof in BuildingSurface:Detailed. Therefore, the roof was recognised as "semi-exterior" surface and 0.0810106[m2·K/W] was used, which resulted in 0.1074271+0.0810106≈0.189[m2·K/W]. After changing Outside Boundary Condition of the roof from Surface to Outdoor, 0.0299387[m2K/W] was used for Exterior Air Film Resistance, and (Interior Air Film Resistance) + (Exterior Air Film Resistance) = 0.1074271+0.0299387 ≈ 0.1373[m2K/W].
For the best answer, please refer to the link that @JasonGlazer attached in his comment. The basis for R-values (Air Film Resistances used to calculate U-Factor with Film) is ASHRAE Standard 90.1 (I-P Edition) Section A9.4.1. Then, the unit is converted from [h·ft2·°F/Btu] to [m2·K/W], and the R-values to the seventh decimal place are used. That's why the R-values are slightly different from the values in ASHRAE Standard 90.1 (SI Edition) Section A9.4.1.
The final answer is:
R-value Condition
All exterior conditions 0.0299387[m2·K/W]
All semi-exterior surfaces 0.0810106[m2·K/W]
Interior horizontal surfaces, heat flow up 0.1074271[m2·K/W]
Interior horizontal surfaces, heat flow down 0.1620212[m2·K/W]
Interior vertical surfaces 0.1197548[m2·K/W]