You can look at the engineering reference for chillers:
And the engineering reference for performance curves:
Usually to calculate the instantaneous capacity, the E+ curve output(s) are multiplied by rated capacity to calculate capacity at part load conditions (i.e. temperatures and airflows that deviate from rated). This is the case for systems like a Single Stage ASHP defined through an AirLoop:HVAC:UnitarySystem. Unsure if that is the case for your chiller models.
"In EnergyPlus, the result of an equation, the dependent variable, represents the response a system or component has given an input (the independent variable) to the system or component model. This response represents the equipment performance related to the mechanism that causes this change (e.g., the change in capacity or power based on a conditional change in temperature, part-load ratio, or other phenomenon). A variety of performance curves are available to describe the most common forms of engineering equations. The coefficients (a-z) in the following equations are entered in the associated curve object to define a specific phenomenon."
Check which specific capacity-related performance curves your chiller model uses, after examining object options in the chillers doc. Check the equations used in the engineering reference and figure out what curve outputs your 500 ton rated capacity is multiplied by to calculate instantaneous capacity.
From eng ref for performance curves:
"Calculating performance curve coefficients in a spreadsheet is a simple matter of finding the data required to perform the regression analysis."
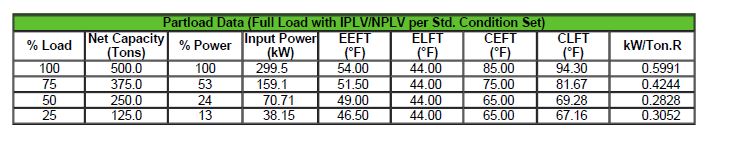
Your x, y, z independent variables for the regression analysis will depend on the curve(s) specifically used by your chiller model object. The example in the performance curves eng ref docs shows x, y as Twb,i and Tc,i, but those are specifically for DX cooling coils; your x, y, z variables will likely be different.
Unfortunately, you need the capacity information at varying x, y, z to perform the regression. Maybe you can use your limited data to extrapolate capacity at different part load conditions?
You can then use excel to perform the regression analysis, as illustrated in the engineering reference, to calculate the coefficients.