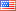
Difference between adiabatic surface and high R value
Hi,
I am trying to minimize conductive heat transfer through the envelope.
I can do this by setting the surface to adiabatic through the measure Set Exterior Walls and Floors to Adiabatic....
Figure 1: Adiabatic Measure with conduction still occuring from ground into building.
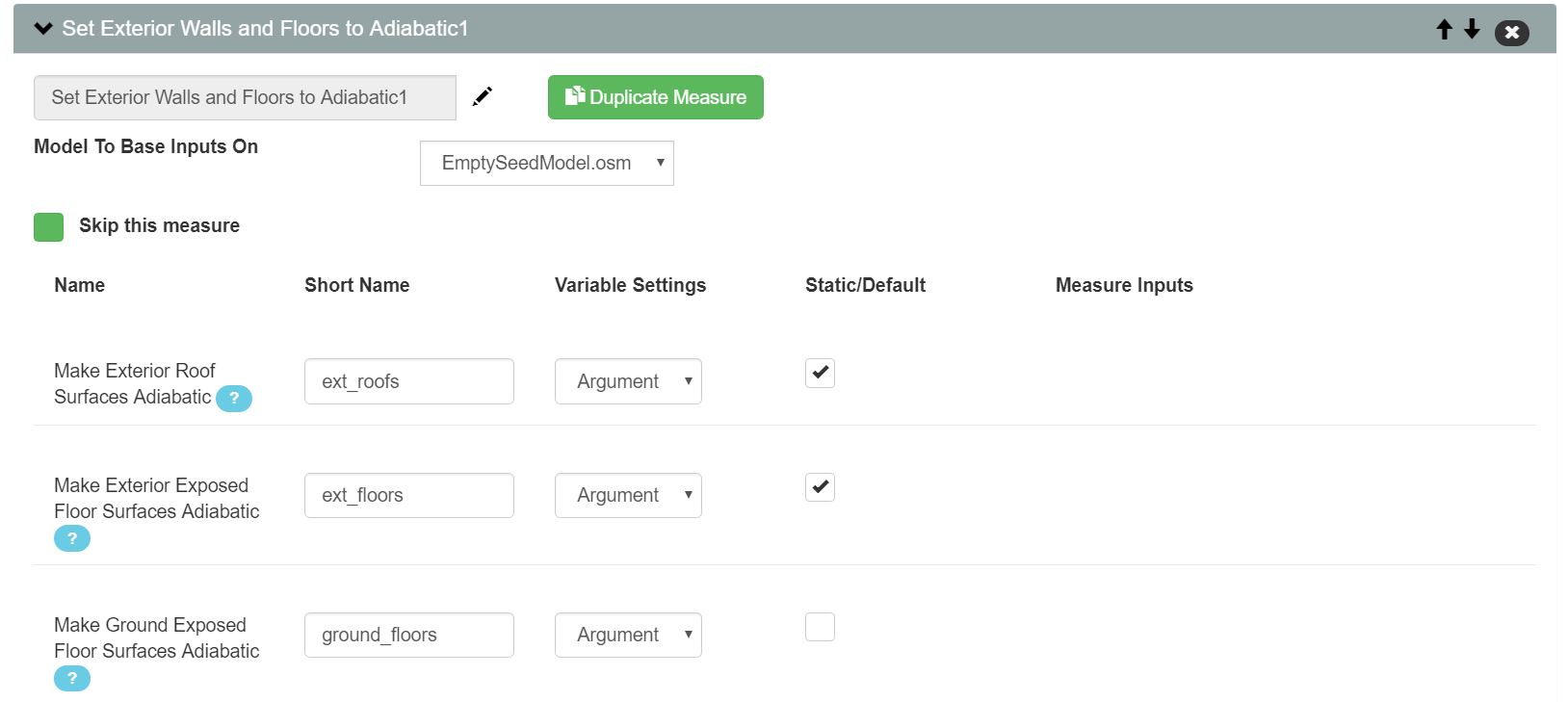
Or, for envelope members that are not the ground (roof and walls), I can increase the R-value to a very high percentage to approximate adiabatic, using the following measure.
Figure 2: R Value Increase Measure with Large (>>100%) Increase.
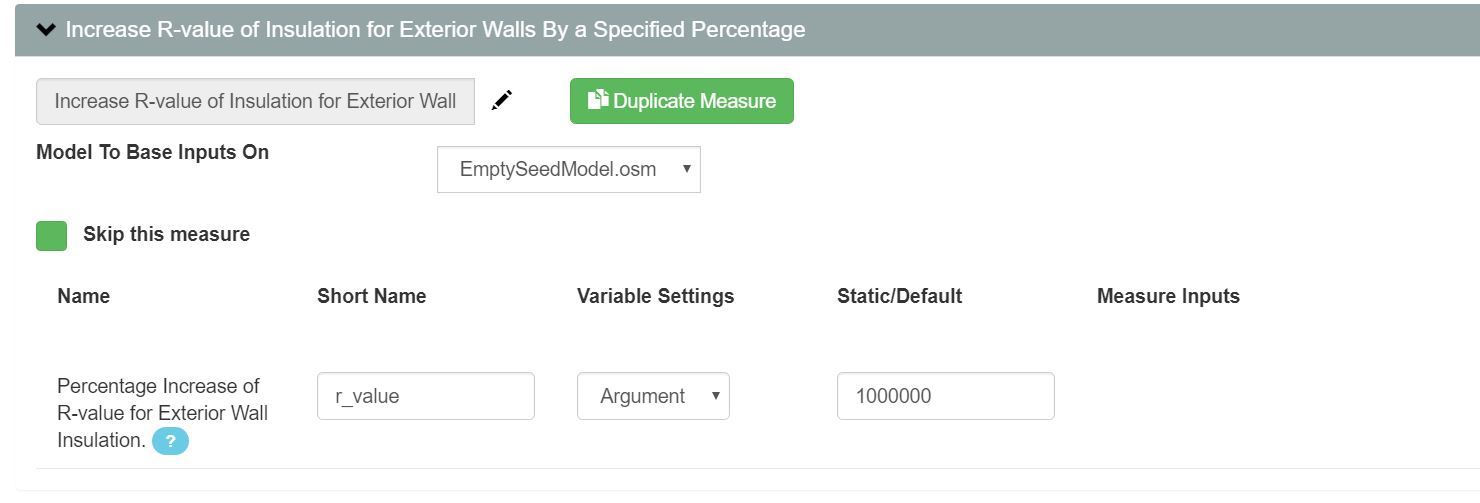
Making a surface adiabatic removes windows and stops ALL heat transfer through that surface.
If I still want fenestration in my walls and solar, radiative, and convective gains on my walls and roofs, can I still use the adiabatic surface measure? I am assuming no, but would like to confirm.
If I cannot set the walls and roofs to adiabatic, what is the max % increase I can input into the above measures without the simulation breaking? @David Goldwasser?