| 1 | initial version |
Based on the numbers I see in your "SlabBTID" file, I think there is something wrong with the thermal conductivity. For example:
2, !- TCON: Slab k {W/m-K}
It basically means that for a 20cm slab, your U value is about 10 W/m2.K. Means the RSI is about 0.1, which is very low.
I hope that helps to solve the problem. If not, let me know and I will look at your file in more details.
 | 2 | No.2 Revision |
Based Mantra, I update my previous answer because it is too long for a comment. Here are a few notes:
1)Changing the 20C has no impact on the number you are looking at (4000W). Because the 4000W is for "cooling load" (see the top of that table). So, the only number that can have an impact on the floor's heat transfer is your cooling setpoint (24C).
2)The section that you check does not report total or annual average heat transfer. It shows the cooling "peak loads". It is just for the peak demand. 3)Basically, this number (4000W) shows that during the peak cooling load, the ground is acting as a cold surface and collects the heat from indoor (that's why it is a negative number).
4)So, the number could be correct. You can check the hourly fluctuations in the indoor air temperature to see when the peak cooling load occurs and that would be the number used to calculate that 4000W.
5)Bear that in mind that these numbers I see in are estimations. Read this for further info.
side note: your "SlabBTID" file, I think there is something wrong with the thermal conductivity. For example:
2, !- TCON: Slab k {W/m-K}
It basically means that for a 20cm slab, heating load is zero. Make sure your U value is about 10 W/m2.K. Means the RSI is about 0.1, which is very low.
I hope that helps to solve the problem. If not, let me know and I will look at your file in more details.
HVAC system is defined properly.  | 3 | No.3 Revision |
Mantra, I update my previous answer because it is too long for a comment. Here are a few notes:
1)Changing the 20C has no impact on the number you are looking at (4000W). Because the 4000W is for "cooling load" (see the top of that table). So, the only number that can have an impact on the floor's heat transfer is your cooling setpoint (24C).
2)The section that you check does not report total or annual average heat transfer. It shows the cooling "peak loads". It is just for the peak demand.
demand.
3)Basically, this number (4000W) shows that during the peak cooling load, the ground is acting as a cold surface and collects the heat from indoor (that's why it is a negative number).
4)So, the number could be correct. You can check the hourly fluctuations in the indoor air temperature to see when the peak cooling load occurs and that would be the number used to calculate that 4000W.
5)Bear that in mind that these numbers are estimations. Read this for further info.
side note: your heating load is zero. Make sure your HVAC system is defined properly.
 | 4 | No.4 Revision |
Mantra, I update I'm updating my previous answer because it is too long for a comment. Here are a few notes:
1)Changing the 20C has no impact on the number with some new info that might help you.
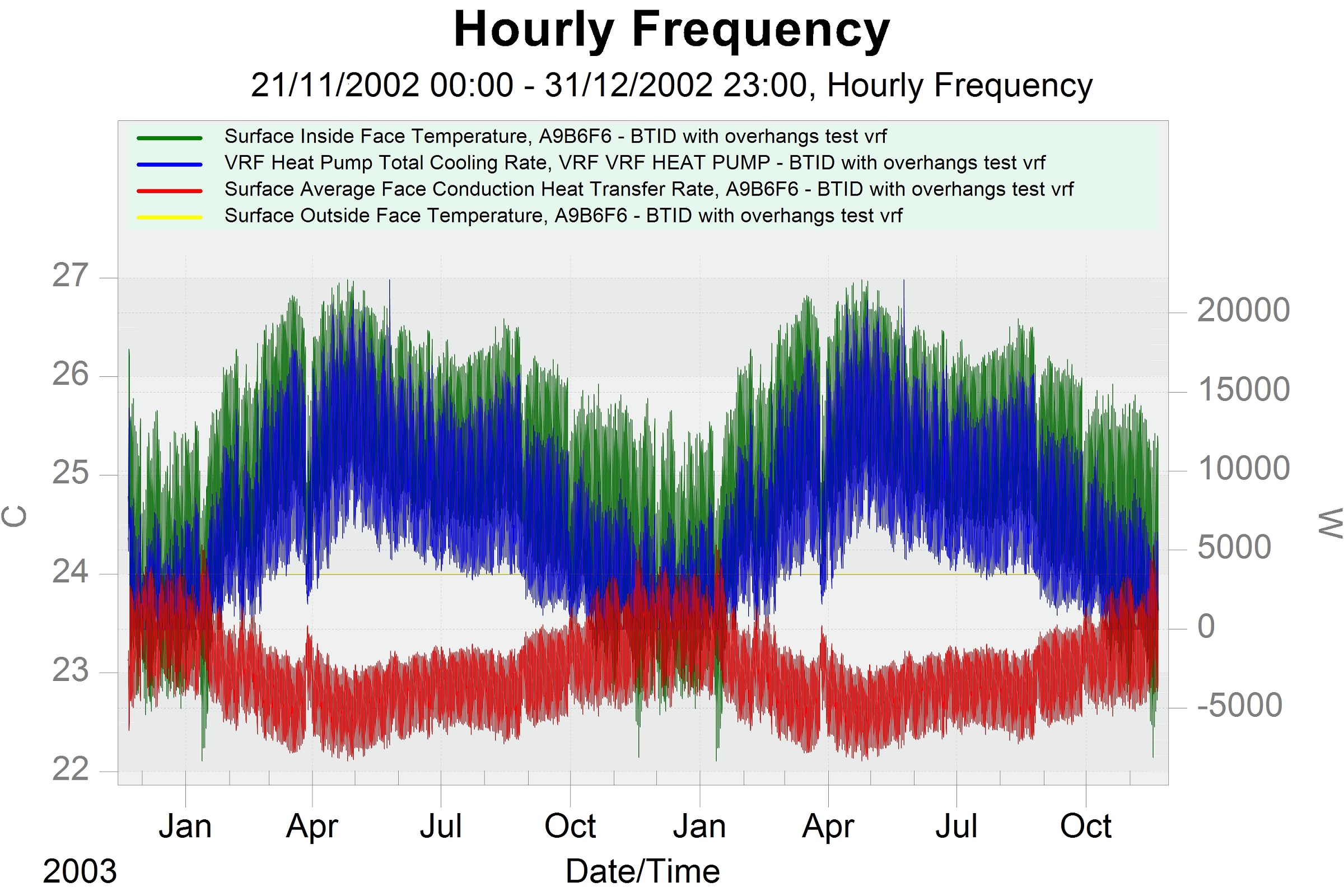
1) In the first figure, you are looking at (4000W). Because the 4000W is for "cooling load" (see the top of that table). So, the only number that can have an impact on the floor's find the outputs related to the "floor's interior surface temp.", "floor's exterior surface temp", "VRF cooling load", and "floor's heat transfer is your rate through conduction". I performed the simulation based on Jodhpur weather file since I didn't have Bali's weather file.
2) As you can see, the cooling setpoint (24C).
2)The section that you check does not report total peak load (blue graph) occurs around May 25th, where the corresponding interior surface temperature is around 26.5C.
3) The yellow line shows that the outside temperature is constant (24C) throughout the year.
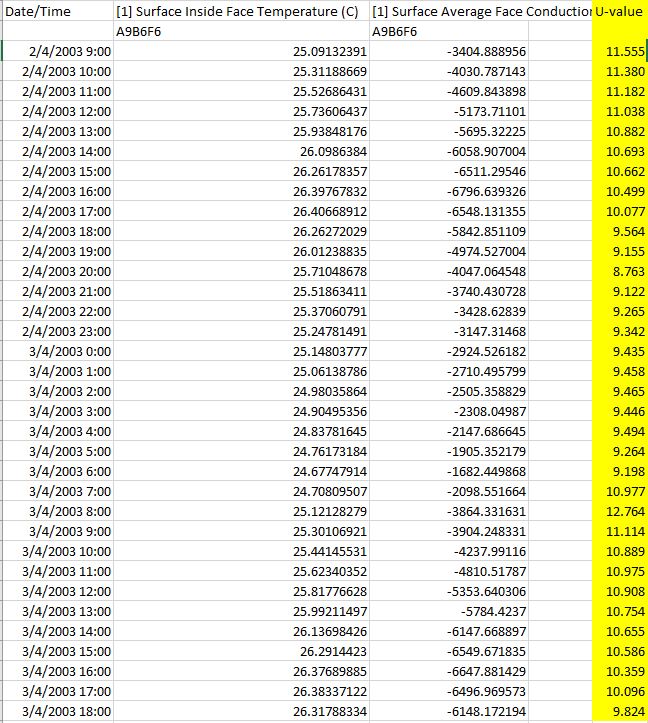
4) The second figure shows a simple calculation based on "heat transfer rate" and the "interior surface temp" exported from the first figure to an Excel sheet. It shows that the U-value is almost constant and it is about 10 W/m2k. The fluctuations are due to the changes in the air film's properties; however, the overall U-value is still very high.
So, it shows that the calculations are correct and whatever is causing the big numbers, is related to the material properties or annual average heat transfer. It shows the cooling "peak loads". It is just for the peak demand.
3)Basically, this number (4000W) shows that during the peak cooling load, the ground is acting as a cold surface and collects the heat from indoor (that's why it is a negative number).
4)So, the number could to be correct. You can check the hourly fluctuations in the indoor air temperature to see when the peak cooling load occurs and that would be the number used to calculate that 4000W.
5)Bear that in mind that these numbers are estimations. Read thismore accurate the conductions. for further info.
side note: your heating load is zero. Make sure your HVAC system is defined properly.